Cattle
Cattle challenge
Cattle face various challenges that can impact their health, productivity, and overall well-being. Here are some common challenges faced by cattle:
- Disease and Health Issues: Cattle are susceptible to various diseases, such as respiratory infections, mastitis, foot rot, and reproductive disorders. Proper disease prevention, vaccination programs, and regular veterinary care are essential to manage and control these health challenges.
- Nutritional Imbalances: Inadequate or imbalanced nutrition can affect cattle performance and health. Challenges include insufficient access to quality forage or feed, mineral deficiencies, mycotoxin contamination in feed, and improper feeding practices. Proper nutrition management, including balanced diets, mineral supplementation, and forage quality assessments, can help address these challenges.
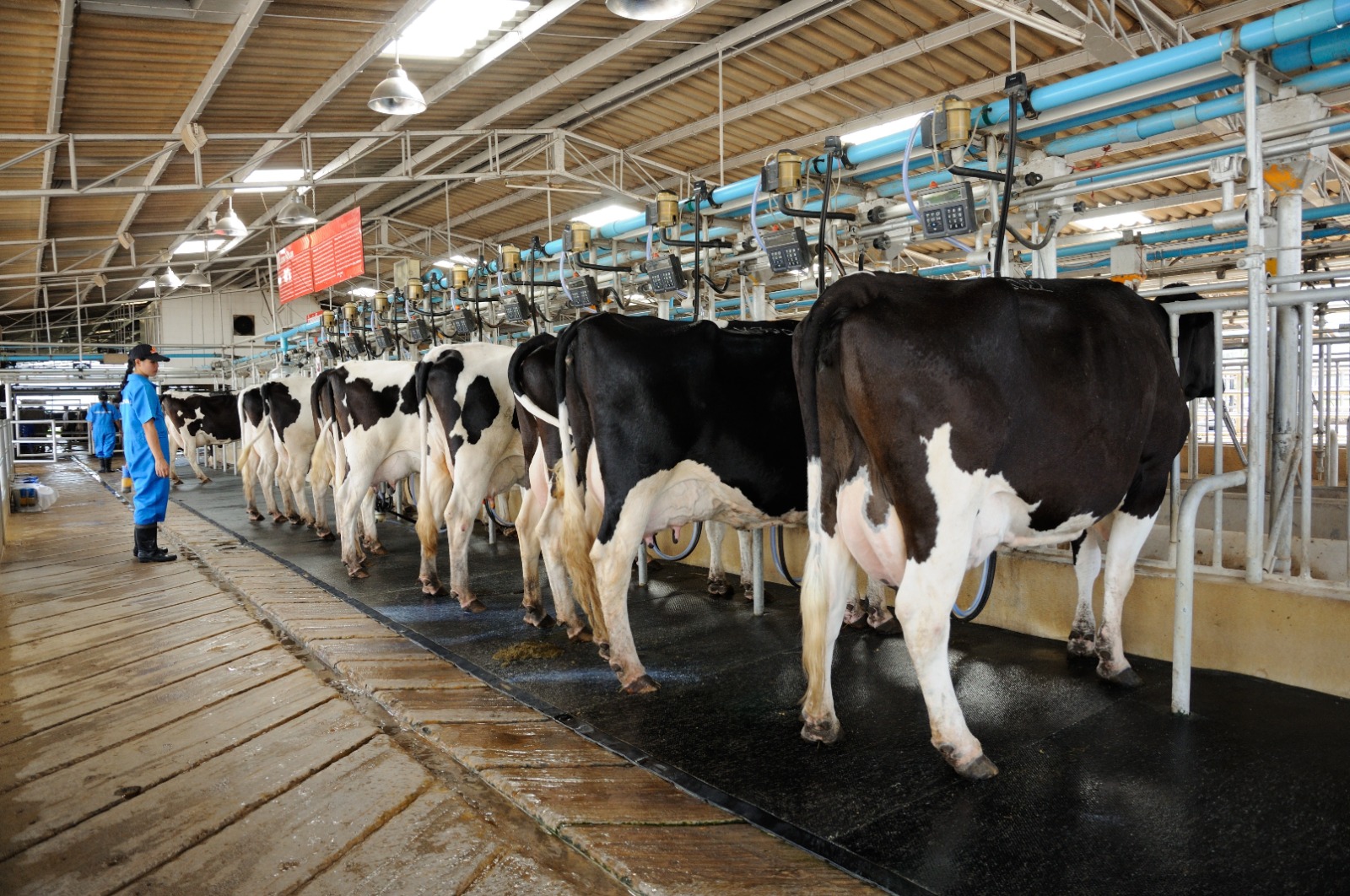

- Heat Stress: Cattle are sensitive to heat stress, especially in hot and humid climates. High temperatures, coupled with inadequate ventilation and access to cool water, can lead to reduced feed intake, decreased milk production, and heat-related health issues. Providing shade, proper ventilation, and access to clean water are crucial to mitigate heat stress.
- Parasites: Internal and external parasites, such as worms, ticks, lice, and flies, pose significant challenges to cattle. Parasite infestations can lead to reduced weight gain, poor feed efficiency, anemia, and skin irritations. Effective parasite control programs, including deworming, use of insecticides, and pasture management, are necessary to minimize these challenges.
- Reproductive Challenges: Reproductive issues, including low conception rates, prolonged calving intervals, and infertility, can impact cattle breeding programs and productivity. Factors such as inadequate nutrition, poor breeding management, reproductive diseases, and genetic factors can contribute to these challenges. Proper reproductive management, including estrus synchronization, regular veterinary monitoring, and genetic selection, can help improve reproductive performance.
- Environmental Stressors: Extreme weather conditions, such as cold, rain, and muddy environments, can create challenges for cattle. These stressors increase the risk of respiratory infections, hoof problems, and reduced feed intake. Adequate shelter, proper flooring, and management practices to minimize exposure to adverse weather conditions can help mitigate these challenges.
- Biosecurity: Maintaining biosecurity is crucial to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases within cattle herds. Biosecurity challenges include the risk of infectious diseases, inadequate quarantine protocols for new animals, and poor hygiene practices. Implementing biosecurity measures, such as isolation of sick animals, vaccination programs, and strict hygiene practices, can help prevent disease outbreaks.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper management practices, regular veterinary care, nutrition optimization, disease prevention, and monitoring. Working closely with veterinarians, nutritionists, and industry experts can help develop tailored strategies to manage these challenges effectively and ensure the health and productivity of cattle.